Before you launch your new website, use our Website Audit Checklist below to improve its performance and security. This checklist includes metrics like page load times, backlinks, crawl errors, and information security best practices.
Of course, using custom mobile application development from professional developers will ensure that your project nails all audits. Even after deploying your project, you’ll want to revisit this checklist periodically.
1. Ensure Information Security
An information security checklist for a website audit goes beyond scanning and removing malicious files. It helps identify malicious threats and their possible impact on the organization. It also allows your development and management teams to focus on high-risk issues and develop practical solutions.
In addition to scanning your website for threats, you should reduce your attack surface area by deleting unused user accounts.

The web app’s login system isn’t the only threat. Don’t forget to audit users with root, SSH, FTP, database, Git, or control panel access. These users may not have direct access through your application’s UI, but they can still get in if you give them too much access to connected tools.
2. Proper Management Of File And Folder Permissions
Starting at the file and folder level, ensure you use the principle of “least privilege” by granting the minimum access required to complete a task.
While it’s tempting to give employees or contractors full administrator access to avoid the headache of developing security protocols, it’s only a matter of time before someone compromises their account.
Run an audit listing all users and their file and folder permissions. Even trusted administrators should have checks and balances to ensure a single user can’t compromise the whole system. Implement user monitoring to keep an eye on changes to access.
Consider using a company password manager like 1Password to share access to protected resources.
3. Content Management System And Comment Settings
If you use a Content Management System (CMS) to run your website or blog, install security tools like iThemes Security Pro to monitor activity, protect against brute-force logins, and monitor your theme and plugins for unexpected file changes.
Remove inactive plugins from your CMS to reduce your attack surface. You can always add them back. Or, for plugins you use occasionally, you can leave them installed but deactivate them to minimize risk and improve website performance.

Hacked websites can ruin your online reputation, and recovering from the incident has substantial financial consequences. The goal is to make your site “uninteresting” to hackers. Locking your doors is a significant deterrent for script kiddies looking to score by taking down your easy-to-hack website.
Invest in managed website hosting solutions like those from 37SOLUTIONS Digital Marketing, including professional security features, automatic updates, and a staging area to test and harden your website.
4. Malware & Other Cyber-Threats
Malicious software has many purposes. Some want to use your website to serve ads, while other security breaches create thousands of backlinks from your website to improve the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) of their client’s websites. Still, others intend to replicate and infect as many targets as possible.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks aim to knock your website or API offline to prevent you from doing business or serving your customers. A DDoS attack will overload your network or servers with garbage traffic from multiple threat actors.

An experienced network engineer can mitigate these attacks, but you must develop a plan ahead of time. The last thing you want to do when your website is down is try to create a solution while everyone is screaming at you.
Keep your website audit checklist updated with the latest plan of action and practice implementing it in mock attack scenarios.
5. Compare Page Load Times
One of the essential steps in evaluating website performance is assessing page load times. A fast page load time is the key to increasing conversions and customer satisfaction. If a page makes a guest wait for more than 3 seconds, you are likely losing customers.
A site’s page load time is the time it takes for content to appear on a page after a visitor lands on it. That is the amount of time it takes to render the most significant piece of visible content on the page. In other words, the faster everything loads and blooms on the screen, the more users it will attract. So, it’s critical to optimize every millisecond of site performance.
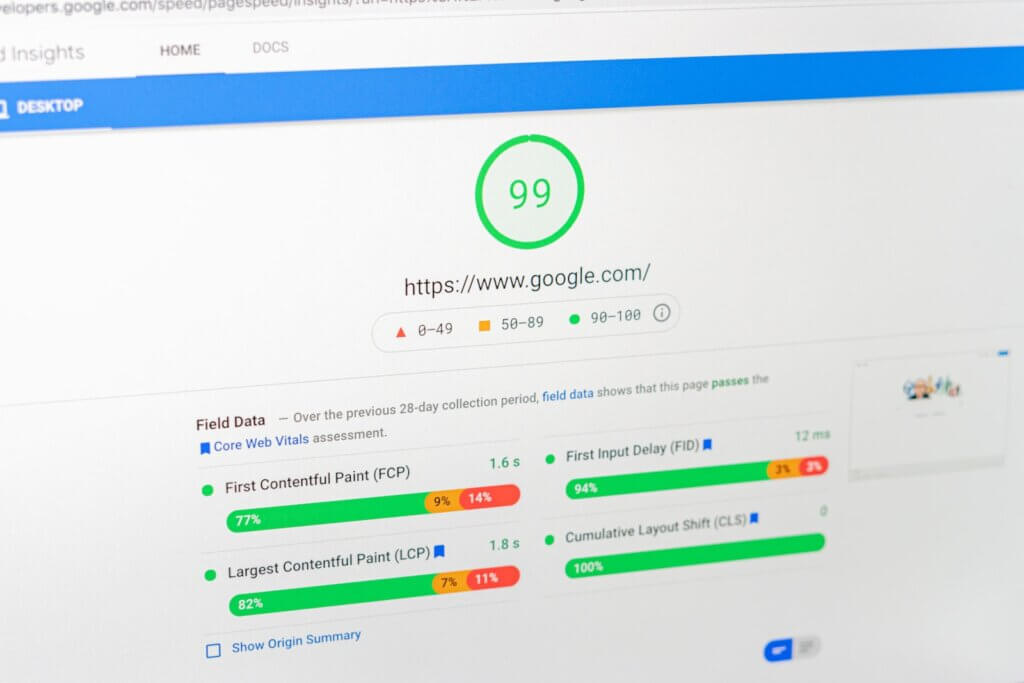
Use free online tools like GTMetrix and Google PageSpeed Insights to measure website performance. Some SEO-focused tools like SEOptimer and SEMrush offer a website audit that includes page speed metrics.
For more advanced applications, use NewRelic or Pingdom to connect monitors directly to your server to access many low-level metrics that will help you squeeze every drop of performance out of your servers.
6. Measure Keyword Performance
Use Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) to monitor your crawl rate. Slow websites with lots of pages will get bogged down by Google’s powerful crawler, so you may need to adjust how fast it crawls your site for the best customer experience.
Monitor your Search Console reports to find the keywords people use to arrive at your site. Monitoring your keywords provides valuable insight into your audience and how they interact with your web application.

Effective keywords increase traffic and visibility, so regularly review and adjust your content to attract your target audience. You’ll see a dramatic increase in traffic by implementing effective keywords.
7. Analyzing Your Website Design (UX)
A site’s design is vital for keeping visitors engaged. According to a Google study, users take less than a second to judge a website’s design.
For general audiences, keep your website simple. Clever or complex websites are challenging to navigate and may drive away customers.
Consider hiring UX reviewers from Fiverr to audit your website. These people visit your website and provide video feedback to help you understand their thoughts as they navigate your site.
8. Check Crawl Errors
Crawl errors differ slightly from measuring your keywords and crawl rate, as discussed in item six above. Crawl errors happen when search engines can’t reach a page they used to visit.
Crawling issues can also occur when the server crashes or becomes unresponsive. If a search engine crawls your website while it’s down or broken, it will mark your content as unavailable. They will eventually crawl your site again, but in the meantime, they may temporarily deindex your page or post.
Long URLs with overly complex folder structures may hinder indexing, too. Keep your URLs relevant but short.
9. Monitor HTML Response Codes (especially 500 errors!)
Every time you visit a web page, your browser receives HTML codes that tell it if the request was successful or not.
Here’s a short list of HTML codes with a generalized description derived from @stevelosh’s funny “HTTP status ranges in a nutshell” tweet:
- 100-199: Keep going; everything is fine so far
- 200-299: Here’s what you requested
- 300-399: Go somewhere else
- 400-499: You messed up
- 500-599: We messed up
A 503 response code means the server was unavailable, and the crawler will return to try again. If your server is constantly overloaded or inaccessible, the crawler will crawl less and may deprioritize your content in favor of others with fast, reliable website hosting.

There are also several ways to fix crawl errors, including following the directions provided by Google’s Search Console. If you have a website that doesn’t have a crawler-friendly URL, you can try a custom 404 error page to let your visitors know.
10. Mind Duplicate Content
Several factors cause duplicate content, including faceted navigation, multiple versions of the same site, scraped content, or copied content. A website audit checklist from popular SEO tools will show you where you can make improvements.
Once you’ve fixed any duplicate content errors, you can start improving your search engine rankings. Some audit tools can automatically find broken links on your site and replace them with internal or external ones on another site, saving you hundreds of hours of manual editing.
Use Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool or their “Test Live URL” feature, formerly known as “Fetch as Google.”
11. Check the Sitemap
Your sitemap lists all your web app’s pages and provides a reference for search engines to crawl your site.
Access your sitemap by typing “/sitemap.xml” after your domain name. Popular SEO tools like Yoast split your WordPress sitemap into smaller, easier-to-digest sitemaps while indexing all of them at “/sitemap_index.xml.” You can adjust which pages show up in your sitemap.
If your sitemap is missing or invalid, there’s a high probability that search engine bots will eventually start ignoring you and hurt your app’s website rank. Sign up for Google and Bing webmaster tools to monitor your sitemap, crawl rate, keywords, and errors. Fix errors as soon as possible to keep your site as high as possible in SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages).
12. Verify Backlinks
When another website links to a page on your website, that’s known as a “backlink.” Backlinks are everything to search engines because they tell search engines who is famous and who needs improvement.
It’s like high school all over again—the popular kids get all the attention, even if the nerds have better content.
A spammy backlink profile will hurt your website and is challenging to remedy. We recommend using professional SEO services from 37SOLUTIONS Digital Marketing to improve your search engine rank. Link to high-quality sites by reaching out to peers in your industry to request a backlink in exchange for some free, high-quality content.

Don’t use Fiverr, iWriter, or Upwork to procure your content unless you have prior experience with quality writers from those platforms. Hire professional writers to create engaging 1500-word articles (no, 500 words is not enough) and give them to the more popular website in exchange for a “do-follow” backlink to yours.
Reading, editing, and publishing articles take time, so the website owner may charge a small fee to have their editor and developer publish your guest post.
If you find some spammy backlinks are hurting your website rank or a Google penalty has recently damaged your reputation, use the “disavow” tool at Google or Bing to remove them. At the same time, reach out to the website owners to have the offending links removed.
In addition to disavowing links, check your page titles. Page titles tell users what they’re reading on the page, which increases the chances of your website being listed high in search results.
13. Email Deliverability
Your website probably needs to send messages to customers about their successful orders or shipping details. These automated messages are called Transactional Emails and are critical to communicating with your customers. They differ from sales, outreach, and support emails in that they are automatic and usually don’t need human interaction.

There are several free online tools, like Mail-Tester, to measure your message’s “deliverability,” or the ability for your message to be delivered and not end up in the customer’s spam or junk folders.
Periodically check your transactional messages to ensure they are successful. Paid services from Mailgun, SendGrid, Postmark, and MailerSend can help improve your deliverability.
Did We Miss Something?
What tools or checklists do you use to prepare your web app to go live? How do you keep your website at peak performance?
Let us know in the comments, and we’ll incorporate your thoughts!




